Introduction
Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) are vital tools for HR process management and optimisation in modern organisations. HRMS enables organisations to perform HR administrative tasks effectively and strategically, while also facilitating strategic planning to enhance organisational efficiency.
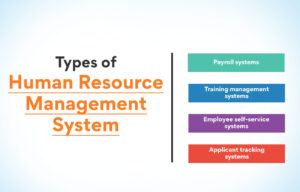
In this blog, we will explore several major types of Human Resource Management Systems and the value that each brings to enhance the HR function and, ultimately, the organisation as a whole.
Overview of Human Resource Management Systems
Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) are nowadays an integral part of organisational management. HRMS aim to automate, control, and integrate Human Resources (HR) management in the workplace.

What is an HRMS, and what does it do?
An HRMS (human resources management system) is an integrated software package that can be used for HR tasks and processes. An HRMS can be utilised for everything from recruitment to employee data management, from payroll to performance management. The main goal of an HRMS is to make HR work easier and more productive and to provide the type of information that can be used to make informed decisions.
Features and Functionalities
HRMS (human resources management system) systems offer a range of features to meet different HR needs. Some of the key functionalities include:
- Employee Record Management: Employees’ details are stored in one central location, safeguarding and streamlining the regular maintenance of all records. HR personnel will be able to monitor an employee’s employment history as well as other pertinent information.
- Payroll Processing: Automated calculation and processing of salaries, tax deductions, and similar payroll activities to ensure employees’ payments are correct and timely, with reduced errors and administrative overhead.
- Attendance and Time Tracking: This functionality records employee attendance or hours worked, keeps track of time off, and ensures compliance with labour laws.
- Benefits Administration: The management of employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. This feature ensures that benefits are seamlessly organised and administered, assisting employees in their enrolment and helping them understand their benefits.
Check out our Human Resource Management Training course on Jobsland.
Benefits of HRMS
The benefits of HRMS (human resources management system) are significant. First and foremost, it is a highly efficient system. It automates repetitive tasks, such as payroll and record-keeping, allowing HR staff to focus more on strategic activities. It enhances the accuracy of your payrolls and record-keeping, eliminating the high risk of mistakes normally associated with manual work. It provides data insights you might otherwise miss through advanced reporting and analytics functions. Lastly, it helps improve employee satisfaction with a self-service portal containing all their information.
Operational Human Resource Management Systems
Operational HRMS is designed to help an HR department perform its administrative and day-to-day work. Such systems are essential to the functioning of basic HR operations.
Automate Mundane Administrative HR Tasks
It’s no coincidence that the most basic operational HRMSs are designed to automate and manage routine HR administrative tasks. The idea is that, at the very least, these systems will allow the HR department to fulfil the vital administrative tasks that keep the business running.

Key Features
Operational HRMS comes equipped with features that streamline various administrative processes:
- Employee Record Management: This feature serves as a central hub for all data related to employees. It stores information such as names, addresses, emergency contact details, recruitment history, education details, performance assessments, and more. This centralised repository also makes it much easier to update employee records and retrieve data as needed.
- Payroll Processing: The automation of payroll is a major advantage of operational HRMS. Such systems calculate salaries, allowances, deductions, and taxes with precision, and generate payslips for employees. This automated process not only reduces errors but also ensures the timely payment of salaries.
- Attendance and Time Tracking: Efficient and productive working hours are key to maximising the potential of any organisation. This feature enables you to track the daily attendance of your employees and manage their time off by providing leave management tools. Further, its integration with Time and Attendance systems helps you calculate and manage overtime effectively.
- Benefits Administration: Keeping track of employee benefits, such as medical, dental, life, and disability insurance, can be a cumbersome process. Operational HRMS can automate the enrolment of such benefits, track the eligibility of employees and dependants, and manage claims. Employees can also access information about their benefits using self-service portals.
Uses of Operational HRMS
Operational HRMS offers several benefits. With these systems, day-to-day tasks can be automated, allowing HR staff to focus more on strategic initiatives. Payroll processes and record-keeping can be streamlined and made more accurate, reducing the risk of expensive mistakes. Operational HRMS also helps the HR department stay in compliance with relevant regulatory requirements, thereby reducing the risk of fines or other penalties.
Tactical Human Resource Management Systems
Tactical HRMS, on the other hand, addresses short-term HR planning and decision-making needs. Tactical HRMS is designed to optimise the recruitment process, regulate employee performance, and facilitate the training and development of employees. In other words, tactical HRMS ensures that companies have the right people with the right skills in the right place at the right time.

Support for Short-Term Planning and Decision-Making
Tactical HRMS offers tools and information that can help HR professionals manage immediate HR needs and make short-term decisions. By emphasising the day-to-day, short-term aspects of HR management, tactical systems ensure that the organisation can react nimbly to changing conditions and short-term objectives.
- Core HR: This module serves as the foundation for all other functionalities of a tactical HRMS. It plays a crucial role in linking HR activities with those of the entire organisation.
- Workforce Administration: This functional area deals with the administration of the workforce, encompassing tasks such as payroll management, benefits management, and time and attendance.
- Performance Management: This functionality enables the HR department to track and assess employee performance, offer guidance, and provide feedback to foster development and growth.
- Talent Management: This function helps HR professionals recruit and retain qualified individuals. It assists in defining the skills and competencies required within an organisation and provides tools for attracting and retaining qualified employees.
- Recruitment and Onboarding: Tactical HRMS assists with the onboarding process, job postings, tracking applications, and screening candidates. Onboarding processes help to ensure that new employees are brought into the organisation smoothly and that all their paperwork and training are completed efficiently.
- Training and Development Management: This system identifies training needs and manages the overall delivery of training programmes. It tracks employee participation, monitors progress, and assesses the effectiveness of training initiatives to ensure that employees have the required knowledge and skills for performing their jobs.
- Performance Appraisal Systems: A tactical HRMS will help you through the process of setting goals, measuring progress, and conducting performance reviews. With the performance appraisal tools included in the system, it is easy to collect feedback, assess performance, and identify areas for improvement. Regular appraisals of performance are crucial for aligning the goals of employees with those of the organisation.
- Self-Service: One of the major benefits of tactical HRMS is that it enables employee self-service. Self-service portals allow employees to view or edit their own HR records, request leave, view benefits, and register for training programmes, thereby shifting administrative work away from HR staff and enhancing employee satisfaction.
Advantages of Tactical HRMS
Tactical HRMS helps efficiently achieve many HR goals. These systems allow us to match the best possible candidates for the required jobs by improving the recruitment and onboarding processes. Training and development are crucial to ensure that once the best candidates are selected, they can develop the necessary skills to contribute to the organisation.
Performance appraisal systems help maintain the required levels of performance in the organisation and ensure that the goals of the organisation guide the efforts of all its employees. Finally, self-service portals empower employees and keep them engaged in the system, providing them with feelings of satisfaction and pride.
Strategic Human Resource Management Systems
Strategic HRMS – human resource management systems – aim to synchronise human resource management with a business’s long-term objectives.

These systems differ from standard HR systems that perform day-to-day HR functions by offering tools and insights to support strategic decision-making and workforce planning.
Enrol our 4-courses bundle Human Resources Management Diploma Bundle.
Alignment with Long-Term Organisational Goals
A well-considered HRMS understands that the future HR needs of the organisation must be strategically aligned with overall business intentions. Standardising and integrating HR data with business strategy allows for forecasting change, effective talent management, and ultimately, the long-term success of the organisation.
Key Features
- Workforce Planning and Analytics: Workforce planning and analytics are the hallmarks of a strategic HRMS. These features help HR teams evaluate workforce trends and future staffing requirements and develop plans to fill any gaps. They can run reports showing headcounts, absenteeism data, or gender mixes and use predictive analytics to decide where to hire, train staff, and plan for succession.
- Talent Management: Talent management is about managing key employees in an organisation. Human capital is a vital resource, and strategic HRMS systems help companies track their talent and monitor the performance appraisal of their employees. Performance appraisal enables the organisation to identify potential high-fliers and develop talent by providing career development plans and succession planning for key roles. Talent management ensures that key employees are motivated and engaged to achieve the company’s aims and goals.
- Succession Planning: Succession planning is vital to the continuity of leadership and the success of the organisation. Strategic HRMS support succession planning by identifying key roles and mapping out succession plans for various jobs. In a nutshell, succession planning is the process of identifying and preparing potential future leaders within a company. HRMS allow for the tracking of the development and readiness of future leaders to prepare the organisation for transitions and leadership changes.
- Organisational Development: Organisational development initiatives are designed to enhance the overall effectiveness and health of the organisation. Strategic HRMS support these initiatives by providing tools for change management, team development, and organisational design. Positive and productive work environments promote the growth and success of the organisation.
Benefits of Strategic HRMS
The benefits of an effective strategic HRMS are considerable. A strategic HRMS allows HR to be more proactive in workforce planning, ensuring the organisation is well-positioned to meet its long-term objectives. It enables workforce planning by providing information about workforce trends and supports talent management by monitoring and addressing potential shortfalls and surpluses. It helps with leadership succession and overall organisational development by fostering a positive work culture.
The Ultimate Guide to Entrepreneurial Success: Business Strategies
Comprehensive Human Resource Management Systems
HRMSs are integrated HR systems that support the full scope of operational, tactical, and strategic HR. They include provisions for all core HR administrative activities as well as strategic workforce planning.

Integration of Operational, Tactical, and Strategic Functionalities
A full-scale HRMS integrates all HRM activities into a single, cohesive system so that HRM is streamlined, data is centralised, and the information that HR professionals need is easily accessible. By integrating operational, tactical, and strategic functionalities, comprehensive HRMS provides an integrated approach to HRM.
Key Features
- Centralised Platform for All HR Activities: A unified HRMS offers a centralised platform that brings together all HR activities in a single system. Activities such as employee record management, payroll processing, recruitment, and performance management can be carried out from one system. This not only simplifies the process but also eliminates redundancy and ensures uniformity across the organisation.
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics: Extensive reporting and analytics are key to obtaining clear insights into HR processes and workforce trends. An advanced HRMS should have powerful analytics tools that help create detailed reports, obtain critical metrics, and review trends to make necessary changes. It aids in data-driven decision-making and strategic planning.
- Customised Workflows and Processes: Every company has different HR needs and workflows. A comprehensive HRMS generally includes a component that enables workflows and processes to be tailored to the company’s specialised needs. This feature ensures that the HRMS fits in with existing organisational processes and can be adjusted as needs change.
- Mobile and Cloud Accessibility: Nowadays, HR professionals are required to perform their functions from anywhere and at any time. Therefore, implementing mobile and cloud access within an HRMS is a critical aspect of a comprehensive system. Mobile and cloud accessibility ensures that employees and HR professionals can access the system from anywhere and at any time, increasing flexibility, promoting remote work, and allowing the HR department to perform their functions without boundaries.
Benefits of Comprehensive HRMS
Comprehensive HRMS offers many advantages. These solutions enable the integration of all HR functions in a single system, leading to streamlined processes and increased efficiency. Centralised data management reduces redundancy and ensures consistency in the management of HR information. Advanced analytics allow the extraction of deeper insights that can be used for strategic decision-making. Furthermore, customisable workflows and mobile access enable increased flexibility, allowing HR professionals to accommodate changing needs and support remote work. Comprehensive HRMS enable organisations to manage human resources more effectively, thereby contributing to organisational success.
Specialised Human Resource Management Systems
These HRMS (human resource management systems) are specific to certain HR functions or industries, and designed to address the particular challenges and requirements of those sectors. They provide customised solutions for specific functions within HR management.

Focus on Certain HR Functions or Industries
Some HRMSs specialise in industries such as healthcare, education, and retail, among others. These software vendors have a deep understanding of the types of HR issues (e.g., staffing, regulatory compliance) and special needs of their sector, and therefore offer features tailored to help manage these unique requirements.
Overview of Advances in HR Technology
Advances in HR technology have led to the development of powerful HRMS software that suits the needs of a wide range of industries. These systems include specialised features for specific industry types.
Niche Solutions Addressing Specific HR Needs
Many of these systems are designed to address the specific needs of HR in a particular sector. For example, healthcare HRMS systems include features for managing the medical credentials of staff and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations. Educational HRMSs are designed to manage faculty records, faculty tenure, and other HR issues specific to academia. Retail HRMSs provide tools for managing a large, often transient workforce, scheduling shifts, and ensuring compliance with retail labour laws.
Examples
- Healthcare HRMS: Systems made for the healthcare sector allow you to track the credentials of medical staff, follow continuing education, and stay in compliance with health regulations such as HIPAA.
- Education HRMS: Maintains faculty and staff records, tracks academic tenure and promotions, and manages special requirements such as faculty scheduling and student-teacher ratios.
- HRMS with a Retail Focus: A retail-focused HR system often includes functionality for managing a large workforce, such as scheduling and time and attendance tracking. It also includes functionality for compliance with retail-specific labour laws.
Integration with Specialised Systems of the Industry
Specialised HRMSs often integrate with other specialised systems to provide a holistic solution. For example, an HRMS for healthcare might integrate with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, while an education HRMS might integrate with Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Advantages of Specialised HRMS
Systems with functionalities customised to industry needs offer great advantages for companies that implement specialised HRMS:
- They ensure the HRMS provides the necessary functionalities to manage and operate HR efficiently and effectively.
- They guarantee compliance with industry regulations, thus avoiding legal problems.
- They allow integration with industry-specific systems, ensuring data accuracy and increasing operational efficiency, which leads to better decision-making and performance.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises Human Resource Management Systems
Organisations that are in the process of selecting an HRMS must decide whether to go with a cloud-based system or an on-premises system.
Ultimately, both have their fair share of features, benefits, and pitfalls, meaning it is important to know the differences and why one option may be better than the other.
Distinctions between Cloud-Based and On-Premises Solutions
The major difference between cloud-based and on-premises HRMS is their deployment and maintenance. Cloud-based HRMS are vendor-hosted, which means they are run on a vendor’s servers and accessed via the Internet. On-premises HRMS, on the other hand, are installed and run on the company’s servers.
Access from Anywhere
Cloud-based HRMS are accessible from anywhere since they are hosted on the Internet. HR functions can be performed from any location, which is especially useful for companies with remote or distributed workforces.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
You don’t have to worry about regular HRMS updates and maintenance when your HRMS is in the cloud. The vendor will maintain a cloud-hosted HRMS. Cloud-based HRMS is a set-and-forget solution because the vendor will update and patch the HRMS, ensuring it remains up-to-date.
Scalability and Adaptability
Cloud-based HRMS are highly scalable. Whether the organisation is growing or downsizing, cloud solutions can be easily scaled up or down to include more users, add functionalities, or increase storage, ensuring the HRMS is always fit for purpose.
Key Features of On-Premises HRMS

Control Over Data
This is one of the most important factors in on-premises HRMS. An on-premises HRMS involves hosting the system within the company’s premises. The company controls data security and privacy. This level of control is crucial for companies with strict data security policies or those in highly regulated industries.
Customisation Options
As the name ‘on-premises’ suggests, organisations that implement an on-premises HRMS tend to enjoy much greater customisation options than cloud-based HRMS users. In an on-premises HRMS, it is much easier for users to integrate with other on-premises systems and customise workflows to accommodate new requirements.
Higher Security
Depending on the cloud-based HRMS vendor, security is robust. However, many organisations still prefer the security of on-premises solutions. Organisations want to be in control of their security protocols. If they can maintain these security standards and comply with internal policies and regulatory requirements, they often feel that an on-premises solution is the right choice.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Cloud-Based HRMS
- Pros: Easy accessibility, regular updates and maintenance, scalability, and reduced IT burden.
- Cons: Dependence on internet connectivity and potential concerns over data security and privacy.
On-Premises HRMS
- Pros: Greater control over data, extensive customisation options, and potential for higher security.
- Cons: Higher upfront costs, ongoing maintenance and support responsibilities, and limited accessibility.
Conclusion
Recognising the four major types of HRMS – operational, tactical, strategic, and comprehensive, as well as the fifth one called specialised – is useful in determining which system would be the most appropriate for your organisation. Each type of HRMS offers distinct features and benefits that can be leveraged to optimise HR efficiency and effectiveness. Remember, choosing the right HRMS for your organisation will be dictated by your specific requirements and, most importantly, by the kind of business and HR outcomes you need to achieve. So do your homework well to determine your needs, and then choose the HRMS solution that supports your goals and, most importantly, enhances your HR capabilities.
The Ultimate Guide to Entrepreneurial Success: Business Strategies
